Messaging chatbots may help businesses improve customer service, sell more, and earn more profit, thanks to a familiar interface and increasing customer interest.
Consumers — your potential customers — use these messaging applications. In 2016, Facebook Messenger, as an example, was said to have about 900 million active users a month. And last year, Business Insider reported that messaging applications had more users than social media networks beginning in about the first quarter of 2015.
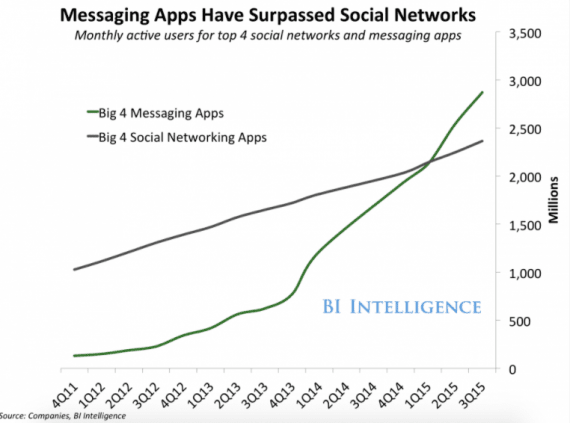
Messaging applications have more active users than the largest social media networks.
As messaging continues to grow in popularity and capability, it follows that consumers will want to interact with brands and services via chat.
2 Basic Kinds of Chatbot Applications
There are two basic categories of modern chatbots.
- Rule-based chatbots that can respond to specific commands.
- Artificial intelligence chatbots that respond to natural language.
An example of a rule-based chatbot may be a basic text messaging application like the ones that some retail businesses use to send coupon codes or offers. You might see a sign at a local coffee shop that says “Text COFFEE to 12345 to get a 10 percent off coupon.”
When your phone’s text messaging system sends the word, “COFFEE,” the application looks at the word, perhaps normalizing it to all lowercase letters, and recognizes it as a command. It then follows a rule the developer wrote and almost instantly sends back the coupon code you want.
If, instead, you sent “I want one of those coupons” to that same chatbot, it would not understand what you wanted. It is simply programmed to respond to the word “COFFEE.” In fact, if you even misspelled that word and sent “COFEE” it might not understand.
Natural language processing, which can be lumped in with artificial intelligence, allows a chatbot application to understand human speech or text messages, including discerning intent.
Thus, when you send the message “I want one of those coupons,” the system is able to understand what you mean or is “smart” enough to ask follow-up questions in response. “Did you want the coffee coupon, the donut coupon, or both?”
It is this second category of intelligent chatbots that represents the greatest opportunity for improved customer service, sales, and profits.
Chatbots are Applications Minus User Interface
Think about an ecommerce website. It is essentially a software application meant to sell products. It has a few aspects or layers that make it work.
- Database. The database stores product information, data about customer and transactions, and most of the content.
- Application layer. This is a set of instructions that gives the application its functionality.
- Application programming interfaces. APIs connect the application to other services to get shipping quotes or process payments, as examples.
- User interface. This is how the user tells your application what he wants or what he is interested in.
An ecommerce website’s user interface is an important part of the overall application. It has amazing product pictures for shoppers to look at. It has an advanced search tool to help the shopper locate products. It has lovely buttons users can click to add products to the shopping cart. And it has forms for entering payment information or an address.
The chatbot — powered by artificial intelligence and natural language processing — has three of these aspects, including the database, the application layer, and access to APIs. But instead of its own user interface, it relies on a messaging platform. It uses Facebook Messenger, Slack, WhatsApp, or similar to interact with the shopper.
This is both a limitation and an advantage.
The chatbot must rely on spoken or written communications to discover what the shopper or user wants and is limited to the messaging platform’s capabilities when it comes to responding to the shopper or user. This requires a much better understanding of natural language and intent. It also means that developers must write connections to several different platforms, again like Messenger or Slack, if the chatbot is to have the same potential reach as a website.
There is a significant upside, though. Your potential customers get to use a familiar interface.
They don’t have to open the web browser on their mobile device and hope your website is responsive. They also don’t need to install your business’s mobile app. They just need to use the same messaging tool they use many times a day. For the consumer, it is easy and familiar.
How Chatbots Work
A natural-language-processing chatbot takes some combination of steps to convert text or speech into structured data that may be used to select the proper response. Here are some of the possible NLP steps.
- Tokenization. Given a string of words (characters), the natural language processor will divide those words into pieces or tokens that are linguistically significant or otherwise useful for the application.
- Named entity recognition. Looks for categories of words, like the name of a product, a person’s name, or an address.
- Normalization. Processes text in an effort to find common spelling or typographical errors that might impact meaning.
- Part of speech tagging. Identifies parts of speech — nouns, verbs — in the text with the aim of understanding complex sentence structures and how those structures impact meaning.
- Dependency parsing. Looks for subjects and objects in the given text to find dependent phrases.
- Sentiment analysis. Watches to learn if the human user is having a good experience or if the chat conversation should be elevated, if you will, to a human operator.
NLP Chatbots Are within Your Reach
When you read through a list with terms like named entity recognition and sentiment analysis, you might think that natural-language-processing chatbots are beyond your business’s current capabilities. If you had to write your own natural language engine for your chatbot from scratch, you might be right. But you don’t have to do that.
There are application programming interfaces and NLP services that do, in fact, put chatbots within reach of most all businesses, small and large.
Building an ecommerce-enabled chatbot for Facebook Messenger will not be as simple as opening up an online store with a SaaS ecommerce platform like Shopify, Volusion, or BigCommerce, but it is not extraordinarily difficult either.
Facebook offers documentation for building your Messenger chatbots and provides an NLP bot engine called Wit.ai that returns nice, neat structured data with customer intent.
The point is that intelligent chatbots have the potential to help improve customer service, boost sales, and increase profits. They are something that many small and mid-sizes business can implement and market.




