Earlier this year at its annual Marketing Live conference, Google announced a slew of Ads updates. One that didn’t receive a ton of attention, but is critical to how advertisers optimize their campaigns, is conversion action sets.
Advertisers use conversion tracking for keywords and ad copy. A “conversion” could be a sale or a visitor filling out the contact-us form. Conversion action sets allow advertisers to establish conversion priorities and optimize accordingly.
Getting Started
Let’s review how conversions are set up in Google Ads. The first step is to decide which conversions to track. Your conversion points may include, for example:
- Sales,
- Contact-us submissions,
- Email signups.
In the “Conversions” section of Google Ads, select where the conversions will occur: a Website, an App, Phone calls, or from another system (Import).
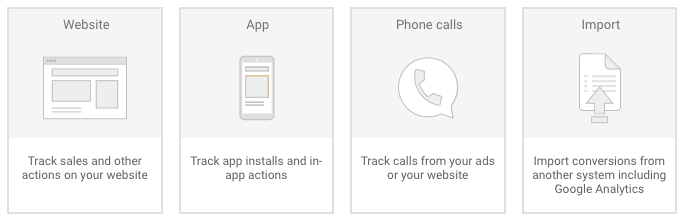
In the “Conversions” section of Google Ads, select the type you want to track.
Say we’re setting up conversions for a website, versus an app or telephone. After clicking the “Website” option, choose your conversion name, category, value (if applicable), source, count, conversion window, and attribution model.
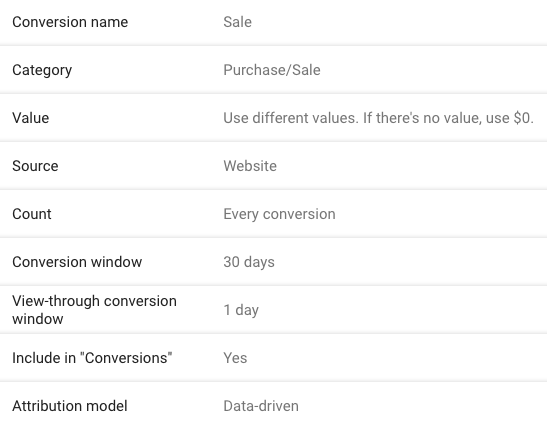
After clicking the “Website” option, choose your conversion name, category, value (if applicable), source, count, conversion window, and attribution model.
Next is the tag setup. You’ll need to install two tags on your site. The first is the global site tag on every page, similar to a Google Analytics tag. The global site tag also facilitates remarketing and sets visitor cookies.
The second tag is the event snippet, which will have a pixel that’s based on how the conversion page renders. Use a “page load” event snippet when the conversion has a unique and separate confirmation page — such as clicking example.com/conversions results in example.com/conversions-thank-you.
Conversely, use the “click event” snippet when the conversion page renders to the same URL. An example is when users click the submit button on example.com/conversions and the page renders to the same URL to confirm. In that scenario, place the click event snippet on the submit button so the click is recorded as a conversion.
By default, Google utilizes account level conversion settings in each campaign. This setting means that Google will list all conversions for each campaign and also use all conversion types for Smart Bidding. Say, for example, that one of your campaigns has 50 total conversions from three conversion actions — purchase (sales), contact-us submissions, and email signup. Though your campaign may have 50 total conversions, the actual breakout could be:
- Five purchase (sales) conversions,
- 25 contact-us form conversions;
- 20 email-signup conversions.
If your primary conversion goal is sales, the campaign has fallen short — only five. Furthermore, if you are using Smart Bidding, such as Target CPA, Target ROAS, or Maximize Conversions, the algorithm is optimizing for all conversions. Google considers them equal. You may experience a higher total number of overall conversions, but the most important goal (sales, in this case) might remain stagnant. This is where conversion action sets are helpful.
Conversion Action Sets
There is a tab in the “Conversions” section called “conversion action sets.” Click “Create Conversion Action Set” to get started.
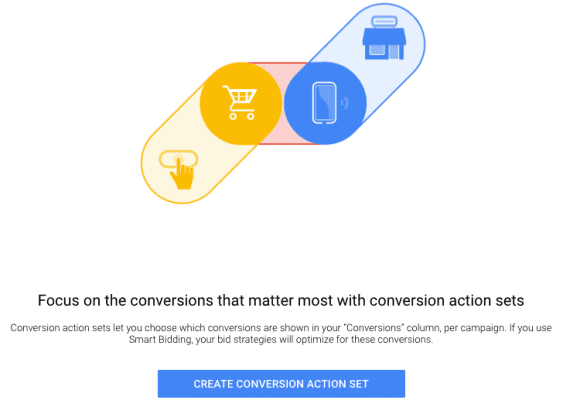
In the “Conversions” section, click “Create Conversion Action Set” to get started.
You can create conversion action sets that fit your strategy. If sales are most important, make that the “Tier 1” conversion action.
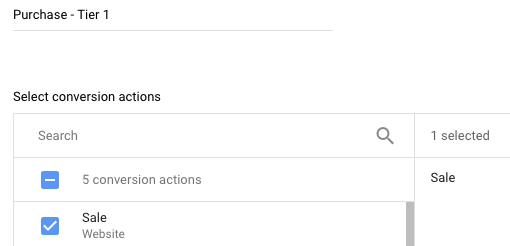
If sales are most important, make that the “Tier 1” conversion action.
Your most important conversions go into Tier 1, the secondary conversions into Tier 2, and so forth. Once you’ve determined these tiers, you can create them as conversion actions sets.
Contact-us submissions and email signups are, in this case, Tier 2 conversions actions. Campaigns that target broad keywords or other top-of-funnel initiatives (such as Display Network campaigns) could also be Tier 2 conversion action sets.
You’ll quickly see the number of sales conversions to optimize Smart Bidding around this set. Note that you can use Google Analytics goals as conversion action sets if imported to Google Ads. For example, to track sales through Google Analytics (in the Google Ads interface), set up this goal as a conversion action set.
Even though you can now segment conversion types, track everything important to your business. This could be, say, a click to a specific product category page or the add-to-cart button.




